We are mere days away from the end of the first quarter, putting us on the precipice of a welcome data deluge. Starting in early April, TechCrunch+ will dig into information relating to startup fundraising in the first quarter.
But we’re an impatient lot, so instead of waiting for the private-market data companies to drop their curated reports, we’ve been doing our own investigating.
The picture forming from Q1 2023 venture data is one of measured decline compared to the end of 2022. Naturally, as we’re looking at first-quarter information a little early, there’s wiggle room in the numbers. March brought with it something akin to a boomlet in domestic venture activity, which could become an even brighter spot if the last bits of first-quarter data further bolster the month’s totals.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money.
Read it every morning on TechCrunch+ or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
That said, the results of our preliminary analysis underscore how far venture activity has fallen from year-ago totals and just how brutal the venture capital market appears for late-stage startups. The largest private-market tech companies are stretched between retreating venture capital totals and an exit market that is effectively switched off.
Let’s walk through an early look at first-quarter venture results, including a monthly breakdown of Q1 2023 investing trends. Then we’ll dig through why “not as bad as we might have expected” from venture activity is thin comfort for starving unicorns. To work!
Save now through June 4 for TechCrunch Sessions: AI
Save $300 on your ticket to TC Sessions: AI—and get 50% off a second. Hear from leaders at OpenAI, Anthropic, Khosla Ventures, and more during a full day of expert insights, hands-on workshops, and high-impact networking. These low-rate deals disappear when the doors open on June 5.
Exhibit at TechCrunch Sessions: AI
Secure your spot at TC Sessions: AI and show 1,200+ decision-makers what you’ve built — without the big spend. Available through May 9 or while tables last.
How’s Q1 2023 venture shaping up?
Today we’ll focus on U.S. venture numbers for a few reasons. First, it’s the dataset I feel the most comfortable sorting through, meaning that I am more confident riffing on it instead of parsing a larger, more global data pile. As the leading venture capital market, the United States plays an outsized role in setting global venture capital trends, so it’s not a bad place to start.
With that in mind, what are we seeing? Here’s all completed United States venture activity, presented on a quarterly basis, via PitchBook data:
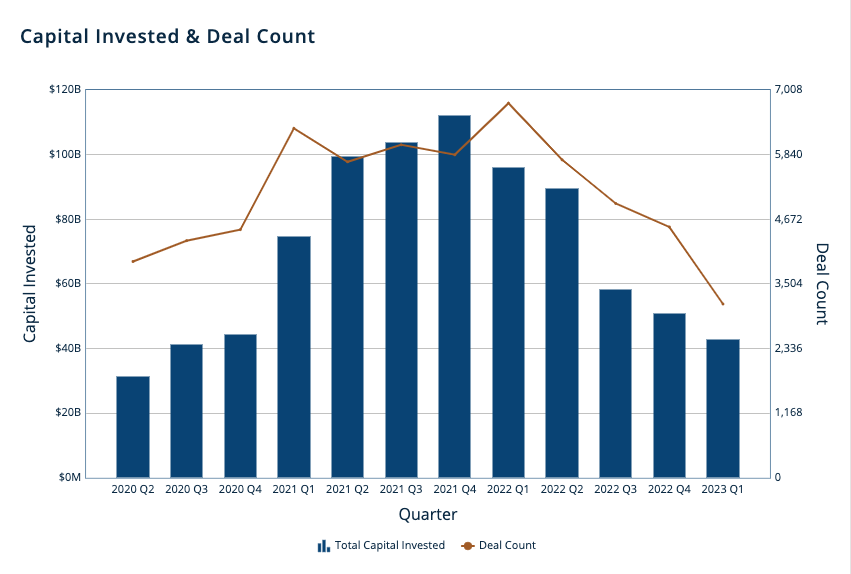
Total capital invested in the first quarter has continued its multiquarter decline. From a year-over-year perspective, we could see a decline of around 55%, with our search terms turning up $96.2 billion worth of venture activity in Q1 2022 and $42.8 billion thus far in Q1 2023. Deal volume is charting similarly, off around 53% in Q1 2023 compared to year-ago results.
Focusing on Q1 2023 versus Q4 2022, we see a sharper decline in deal volume than dollar volume, but given how closely both figures land in terms of their declines measured on a year-over-year basis, we shouldn’t read too much into the discrepancy between sequential-quarterly changes and year-over-year differentials.
In fact, I had expected a sharper decline in the first quarter of this year compared to the fourth of last year, given how much turmoil and angst we’ve seen to start 2023. Instead, we’re seeing similar declines to what we saw in the back half of 2022; perhaps the most aggressive declines in sequential-quarterly venture activity are behind us, at least domestically.
There is even some good news in the above. If you break the above quarters into months, January and February were the worst two in terms of the value of U.S. venture deals for years. But March did better, posting thus far the strongest single-month total of domestic venture deal value since October 2022.
One month is not a trend, but March 2023 does indicate that it is possible for the regular declines in venture deal value to revert.
Q1 2023 isn’t as bad as we might have expected, and there’s even some good news inside the quarter itself. None of that, however, does away with the fact that the total number of venture deals and their dollar-measured value are set to fall around 50% compared to year-ago totals. That’s particularly bad news for one startup group.
Metrics
One thing that the PitchBooks and CB Insights and Crunchbases of the world like to do is build signal from their data. One way that PitchBook, in particular, likes to slice and arrange its information is to calculate how much capital a particular startup cohort needs to operate and how much is being invested in that same group.
Per PitchBook’s Q1 2023 Quantitative Perspectives report (updated in March), here’s the current set of those metrics as of the end of February (the higher the multiple, the greater the gap between capital needs and capital raised):
- Early-stage: 1.8x.
- Late-stage: 2.8x.
Notably, that 2.8x figure is getting worse over time. A separate piece of PitchBook data had the same data point pegged at 2.5x at the end of 2022.
Of course, I don’t think that every startup in the United States that raised early- or late-stage venture capital will make it. However, per PitchBook’s internal math, later-stage startups are more troubled than their early-stage peers.
It’s even worse for a startup cohort that we expected to lead an eventual IPO charge when the public markets shook off their recent malaise: software companies.
Per the same PitchBook report, software startups in 2023 (through February) need around 3.2x the capital that is coming into their accounts from venture investors. Again, amend the number slightly, but it’s still a staggering figure.
Recall that before Silicon Valley Bank imploded, creating a rip in financial space-time, it noted in a report to its investors that startups were raising less but not moderating their burn too much. Cross that with the above information, and we have a crisis. I honestly don’t know what late-stage software startups — of which there are so very many companies — are going to do.
It turns out burn reduction at startups is more aspiration than reality
Alternative funding methods are also drying up: SPACs are dead, M&A is moribund, there are no IPOs and debt is more expensive than it has been in a decade. Given limited burn reduction and worsening fundraising conditions, you almost wonder if late-stage software startups know something that we don’t.